
Simplified model of replication fork Download Scientific Diagram
The process of semiconservative replication suggested a geometry for the site of DNA replication, a fork-like DNA structure, where the DNA helix is open, or unwound,. Replication Fork Barriers (RFBs) control DNA progression to protect genomic integrity. RFBs allow for the coordination of DNA replication with important processes on chromatin.

Model of a replication fork showing leading and lagging strand... Download Scientific Diagram
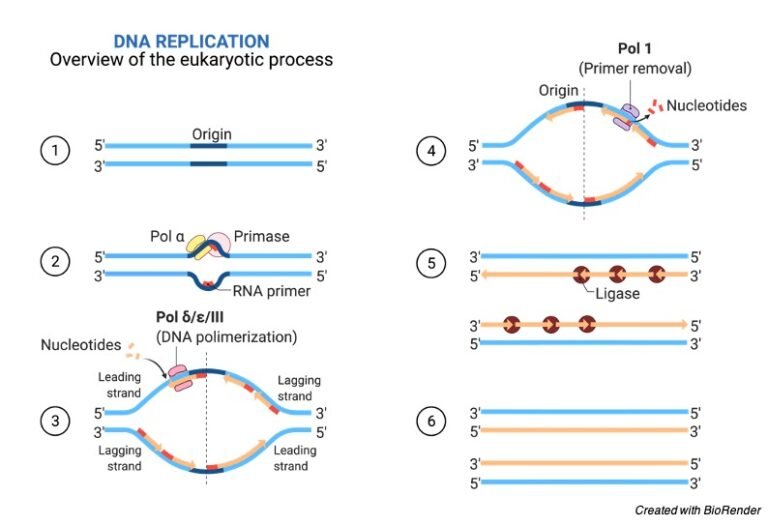
Replication in prokaryotes starts from a sequence found on the chromosome called the origin of replication—the point at which the DNA opens up. Helicase opens up the DNA double helix, resulting in the formation of the replication fork. Single-strand binding proteins bind to the single-stranded DNA near the replication fork to keep the fork open.

DNA Replication Fork Definition & Overview Video & Lesson Transcript
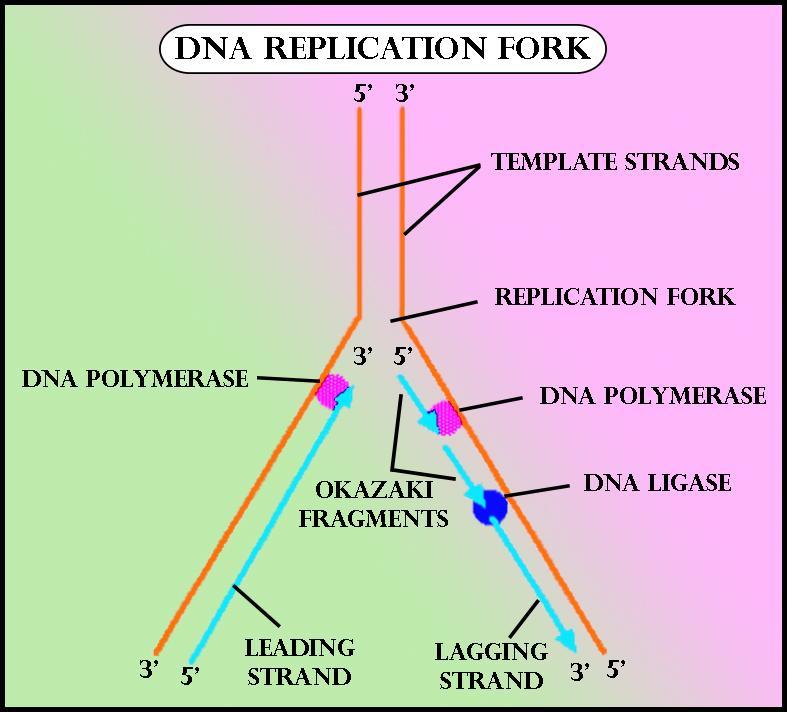
The replication of the other strand, which runs in the 5′ to 3′ direction away from the fork, is made discontinuously. It happens because as the fork moves forward, the DNA polymerase (which is moving away from the fork) comes off and then reattach to the newly exposed DNA. This strand is called the lagging strand.
Replication fork structures acted upon by DNA helicases. A) WRN [72]... Download Scientific
During replication the two strands of DNA separate; the resulting structure is called the replication fork. The replication fork forms because enzymes called helicases surround the DNA strands and break the hydrogen bonds which hold them together. The result is that two long branches, almost like fork prongs, each of which is a DNA strand.
[Solved] Draw a schematic diagram of the replication fork, showing Both... Course Hero
What is the replication fork in DNA? The replication fork is a Y-shaped structure. It forms at the repication bubble with the help of the enzyme DNA helicase. What causes replication fork?.
DNA Replication AP® Biology Crash Course Review Albert.io
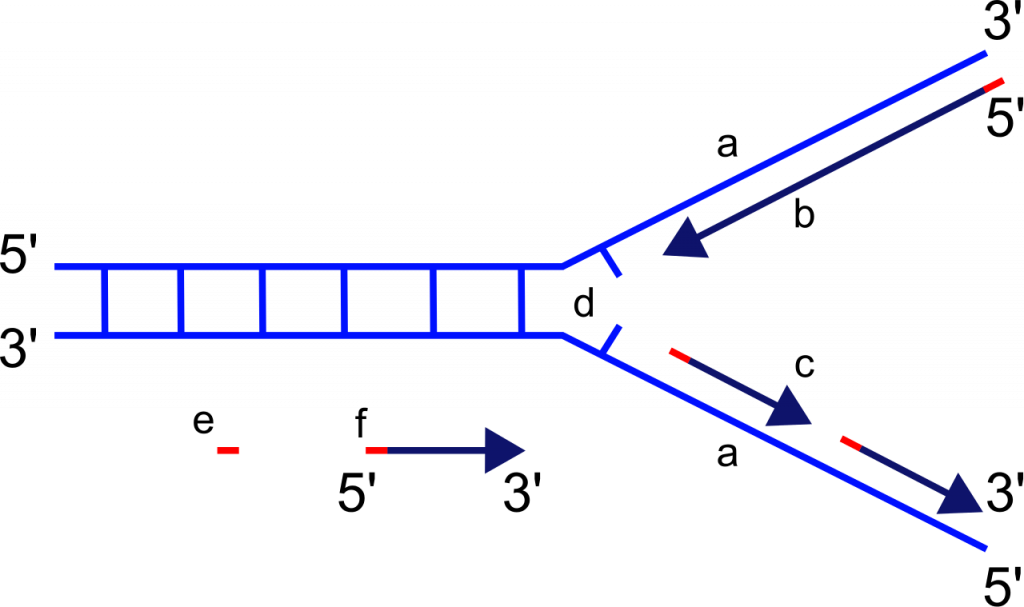
The replication fork moves at the rate of 1000 nucleotides per second. DNA polymerase can only extend in the 5′ to 3′ direction, which poses a slight problem at the replication fork. As we know, the DNA double helix is anti-parallel; that is, one strand is in the 5′ to 3′ direction and the other is oriented in the 3′ to 5′ direction.
Draw a labeled diagram of a replicating fork.
In molecular biology, [1] [2] [3] DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. [4] DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part of biological inheritance.
PPT DNA Replication PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2591641
When a cell divides, it is important that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the DNA. This is accomplished by the process of DNA replication. The replication of DNA occurs during the synthesis phase, or S phase, of the cell cycle, before the cell enters mitosis or meiosis. The elucidation of the structure of the double helix.

Replication Fork Diagram Quizlet
The replication fork is a structure which is formed during the process of DNA replication. It is activated by helicases, which helps in breaking the hydrogen bonds, and holds the two strands of the helix. The resulting structure has two branching's which is known as prongs, where each one is made up of single strand of DNA.

Similiar Replication Fork Diagram Keywords Dna, Dna molecule, Dna helicase
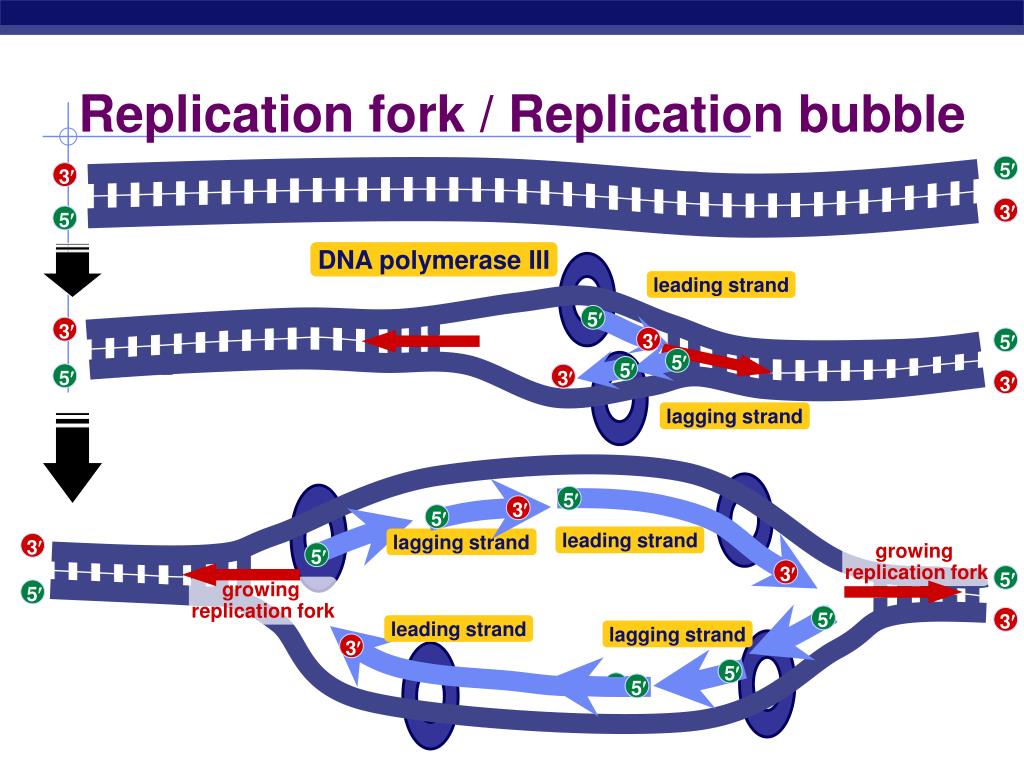
At a replication fork, the DNA of both new daughter strands is synthesized by a multienzyme complex that contains the DNA polymerase . Figure 5-6 Two replication forks moving in opposite directions on a circular chromosome.

Dna replication fork. Biology lessons, Teaching biology, Biomedical science
What Happens at the Replication Fork? Two main activities happen at the fork: DNA unwinding and DNA synthesis. The RF unwinds the unreplicated DNA ahead of it through a helicase enzyme.
Replication Fork Definition, Structure, Diagram, & Function
Key points: DNA replication is semiconservative. Each strand in the double helix acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. New DNA is made by enzymes called DNA polymerases, which require a template and a primer (starter) and synthesize DNA in the 5' to 3' direction.
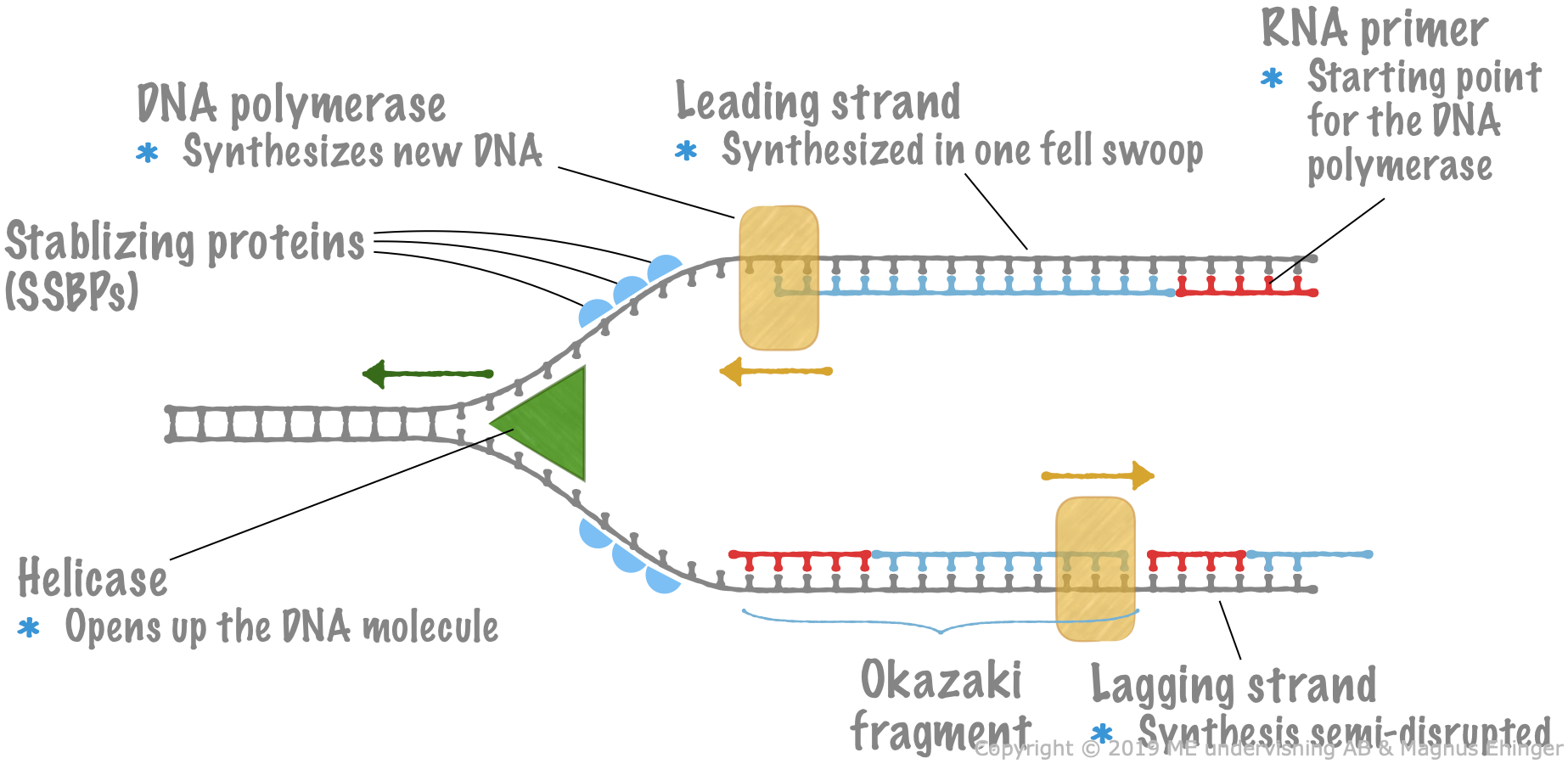
Replication Of Dna
During DNA replication, both strands of the double helix act as templates for the formation of new DNA molecules. Copying occurs at a localized region called the replication fork, which is a Y shaped structure where new DNA strands are synthesised by a multi-enzyme complex. Here the DNA to be copied enters the complex from the left.
A, schematic representation of the replication fork. Polymerase III... Download Scientific Diagram
Key Terms. origin of replication: a particular sequence in a genome at which replication is initiated; leading strand: the template strand of the DNA double helix that is oriented so that the replication fork moves along it in the 3′ to 5′ direction; lagging strand: the strand of the template DNA double helix that is oriented so that the replication fork moves along it in a 5′ to 3′ manner
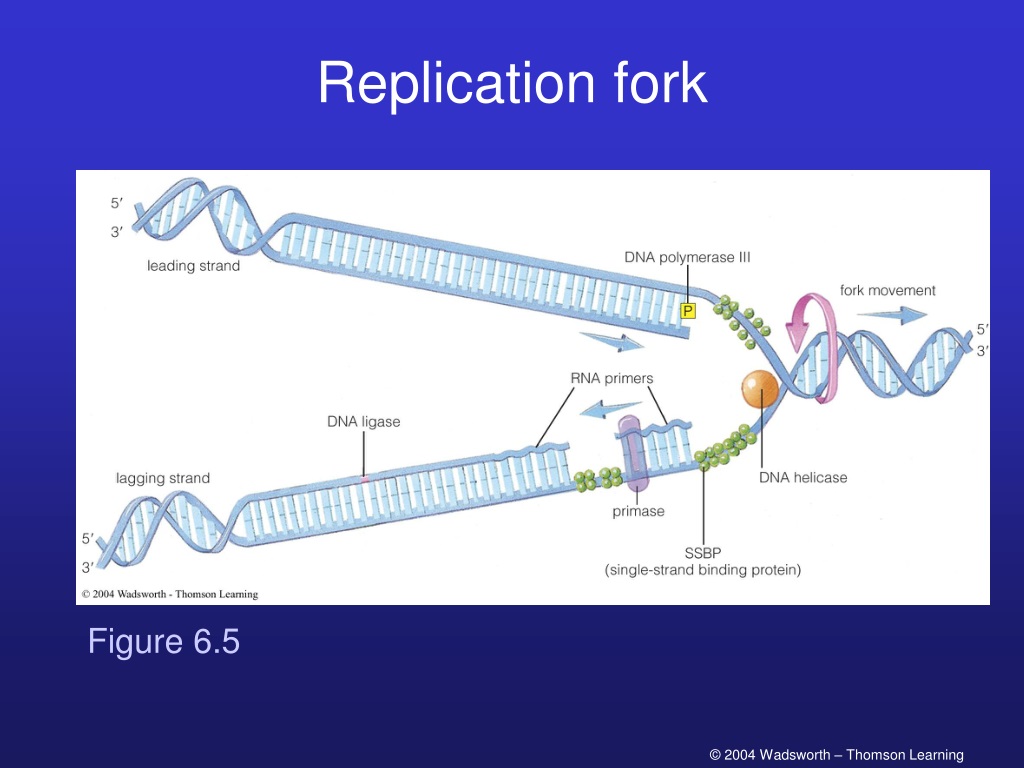
PPT Chapter 6 The of PowerPoint Presentation ID9491318
9: Molecular Biology 9.2: DNA Replication Page ID OpenStax OpenStax When a cell divides, it is important that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the DNA. This is accomplished by the process of DNA replication.

DNA Replication Fork. YouTube
After replication forks are reversed into a 4-way structure and DNA damage is bypassed or repaired, cells need a way to restart DNA replication and restore the replication fork. In addition to using HR ( Figure 2f ), fork restoration can also be accomplished by migrating the reversed fork back into the 3-way junction ( Figure 2e → c ).